Multiple Choice
Select the correct answer.
1. Which of the following is an example of human capital?
A. Investing in agricultural production.
B. Investing in automation.
C. Investing in education.
D. Investing in roads and bridges.
E. Investing in new factories.
2. From 1948 to 1971, the value of the U.S. dollar compared to other currencies…
A. ...floated freely according to buying and selling in currency markets.
B. ...had a managed float in which the U.S. government sometimes intervened in currency markets to maintain its value.
C. ...was fixed to the British pound.
D. ...was pegged at $35 per ounce of gold.
E. ...was valued according to price at which gold traded.
3. Jefferson's embargo, which inadvertantly spurred industrialization in the USA, is an example of which development policy?
A. Export-led growth.
B. Growth by asphyxiation.
C. Import substitution.
D. Micro loans.
E. Primary commodities export.
4. What is the implication of the “demographic transition” during economic development?
A. Birth rates and death rates fall at the same rate as a state becomes more developed.
B. Population growth explodes in the early stages of development, making it easier to develop further.
C. Population growth explodes in the early stages of development, making it harder to develop further.
D. Population growth falls in the early stages of development, making it easier to develop further.
E. Population growth falls in the early stages of development, making it harder to develop further.
5. Which of the following is closest in spirit to the idea of “sustainable development”?
A. Exporting only raw materials
B. Managed forestry
C. Slash and burn clearing for farms
D. Strip mining
E. Unrestricted fishing
6. Which of the following countries is NOT a member of NATO but is a member of the European Union?
A. Ireland
B. Denmark
C. Norway
D. Romania
E. Switzerland
Definitions/Fill in the Blank
Type in the correct terms for the following sentences.
7. When the infrastructure of a country is set up primarily for the export of some commodity, we call this a(n) .
8. A(n) is a state institution that controls the discount rate charged commercial banks and other aspects of monetary policy.
9. A group of countries actively working together to manipulate the price of a commodity is called a(n) .
10. is a set of ideas for development that roughly follow the example of English economic history.
11. Commodities that are grown for their export value--such as tobacco, coffee, and even opium--and more generally known as .
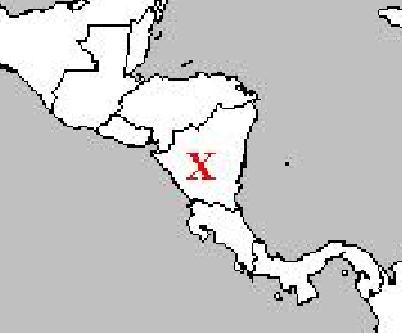
12. Identify the marked country below: .
