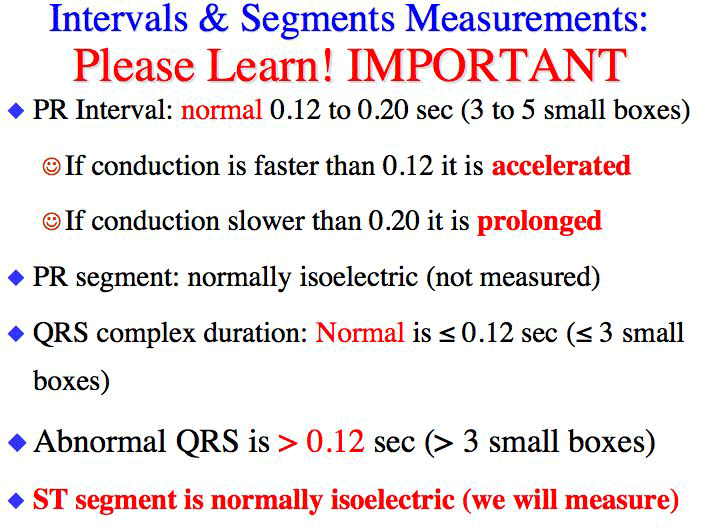
| Sept. 14-18: PQRST Labeling, Intervals, Segments, and Complex Measurements, Review of Regular and Irregular Heart Rate Measurement, Calibration, PRI and QRS Measurements OBJECTIVES: Be able to correctly label the inervals, segments, complex and J point of the PQRST cardiac cycle Be able to do the R wave to R wave heart rate method very effectively Be able to do the 6-second heart rate method very effectively Be able to fine tune your skills for an EKG rhythm check (Regular or Irregular) Be able to identify the calibration on the EKG 12-lead Begin learning how to do accurately PRI and QRS measurements (this takes a lot of practice to get really accurate) Class, Please download the EXAM FIRST. We are working through all Exam questions in the YOUTUBE video lectuers. Click Here to Download Exam 2 Part A due Friday Sept 18 by 12 Midnight Please CLICK the links below and PRINT: |
||||||||
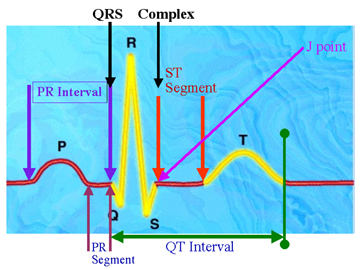
| Intervals, Segments, Complex & J Point | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
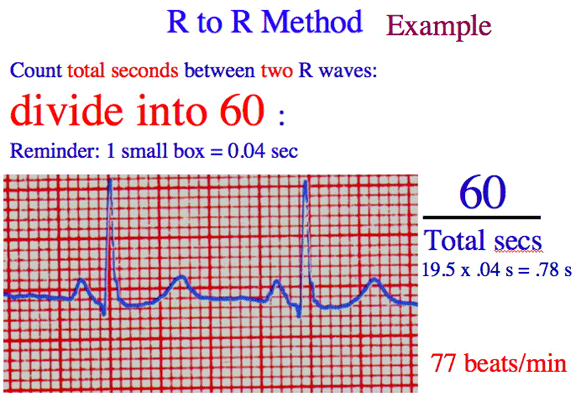
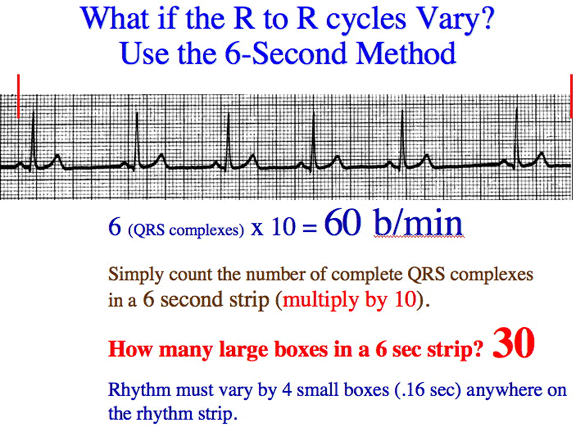
| Let's REVIEW and PRACTICE our Rhythm Strip Measurement Techniques and Fine Tune our 6-Second and R to R Heart Rate Measurement Techniques | ||||||||
| Click here for the EKG 'R wave to R wave' and '6-second' review and Exam Questions YOUTUBE lecture video |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
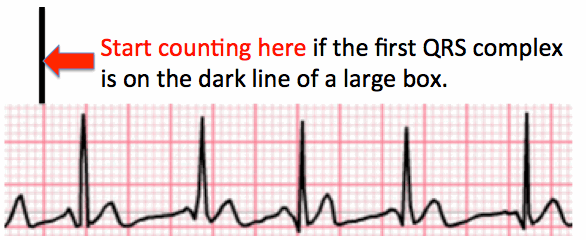
| Where to start counting on an irregular rhythm? | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
| The first QRS complex of this irregular rhythm is on the dark line of the large box. Note where you start counting to determine the 6-second heart rate for an irregular rhythm. | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
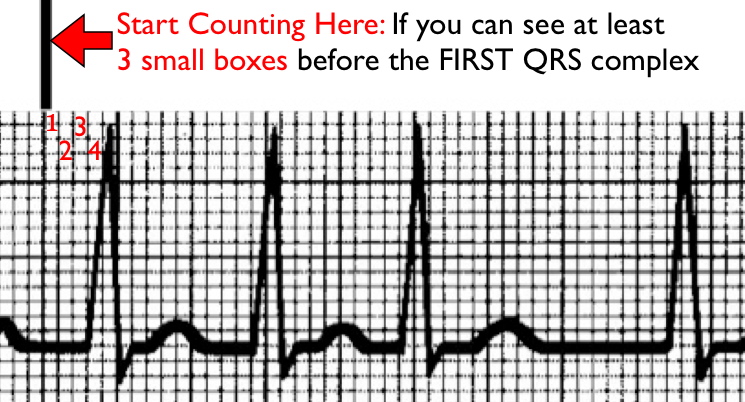
| Note, with this irregular rhythm there are at least 3 small boxes before the FIRST QRS complex AND the line of the LARGE BOX. In fact, in this example we see 4 small boxes. So you start your counting of 30 large boxes at the starting point containing that first QRS complex. | ||||||||
| Let's Learn How to Calibrate Voltage on an EKG 12-Lead and Fine Tune our Mean QRS Axis and Rwave Transition Interpretations | ||||||||
| Click here for the EKG Calibration YOUTUBE lecture video |
||||||||
| Let's Learn How to do the PRI and QRS Measurements | ||||||||
| Click here for the PRI and QRS YOUTUBE lecture video |
||||||||
| PRI and QRS Measurements: Please practice a LOT and you will get very good at these measurements...but you MUST PRACTICE! Also, for true accuracy go ahead and count 1/2 boxes if present. |
||||||||
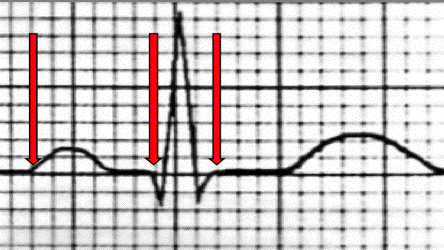
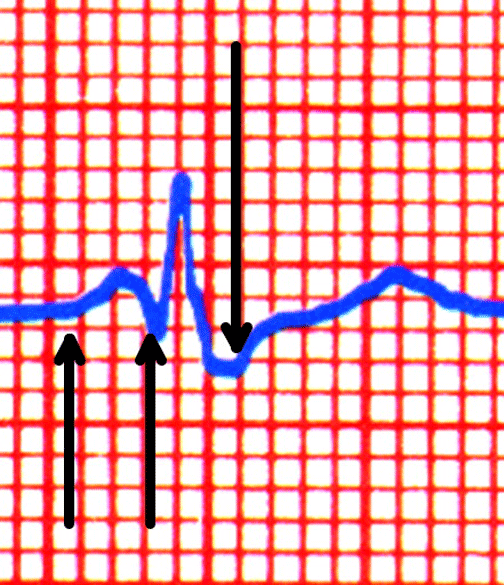
| The PRI measurement is from the point where the Pwave deflects from isoelectric to the beginning of the Qwave. If no Qwave is present, the end of the PRI is at the beginning of the Rwave. The QRS is from the beginning of the Qwave (or Rwave if no Qwave is present) to where the Swave returns to isoelectric (which is the J point). |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
| The PRI above is 6 small boxes (.24 seconds) = prolonged | ||||||||
| The QRS is 3 small boxes (.12 seconds) = normal | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
| The PRI above is 2.5 small boxes (.10 seconds) = accelerated | ||||||||
| The QRS above is 3 small boxes (.12 seconds) = normal | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
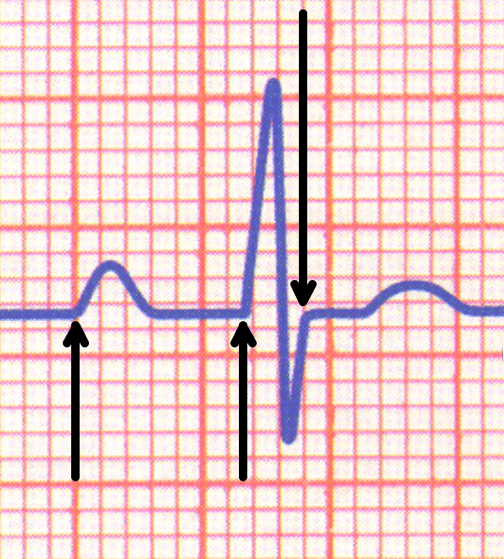
| The PRI above is 7 small boxes (.28 seconds) = prolonged | ||||||||
| The QRS above is 2 small boxes (.08 seconds) = normal | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||
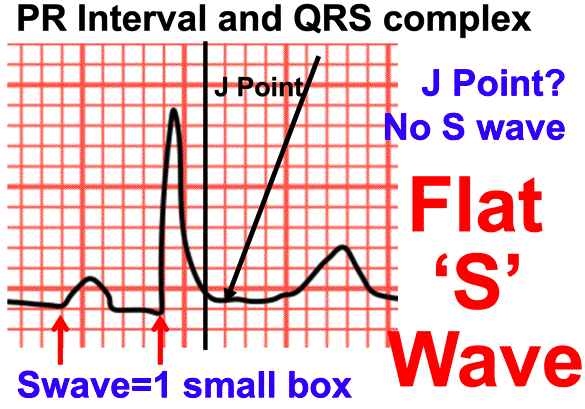
| How to Measure QRS when there is a Flat 'S' Wave | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
| In the PRI above there is no Q wave so going from the inflection of the Pwave to inflection of the Rwave you get a PRI of 5 small boxes (.2 seconds) = normal | ||||||||
| The Flat 'S' wave poses a real challenge. Here are the steps: | ||||||||
| 1) Follow the Rwave until it reaches isoelectric or (as above) it starts to go toward the Twave | ||||||||
| 2) Mark the point where the Rwave begins to go towards the Twave | ||||||||
| 3) Move over 1 small box from your mark; that is the J point | ||||||||
| 4) You can now measure the QRS; for the above it is 3 small boxes (.12 seconds) = normal | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
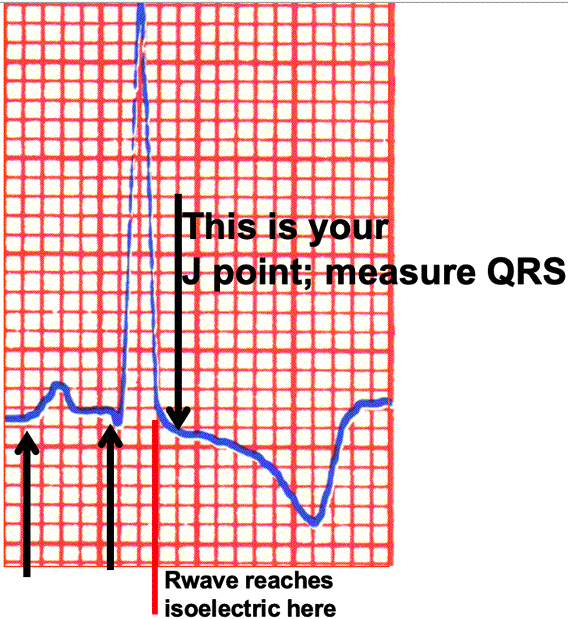
| The PRI above is 4.5 small boxes (.18 seconds) = normal | ||||||||
| The Swave is not present due to the inverted Twave. Use the same technique as with the Flat 'S' Wave | ||||||||
| 1) Follow the Rwave until it reaches isoelectric: I have marked it with the red line | ||||||||
| 2) Move over 1 small box from where the Rwave reaches isoelectric: that is your J point | ||||||||
| 3) You can now measure the QRS; for the above it is 3 small boxes (.12 seconds) = normal | ||||||||
| Exam 2 Part A: Click here to get questions: Exam 2 Part A is due by 12midnight on Sept 18. No late papers accepted. |
||||||||
|