Determining Rheobase and Chronaxie From a Strength-Duration Curve
The following diagram will assist you in calculating rheobase and chronaxie for your nerve. The numbers adjacent to the dashed lines and arrows indicate the order in which you make the measurements.
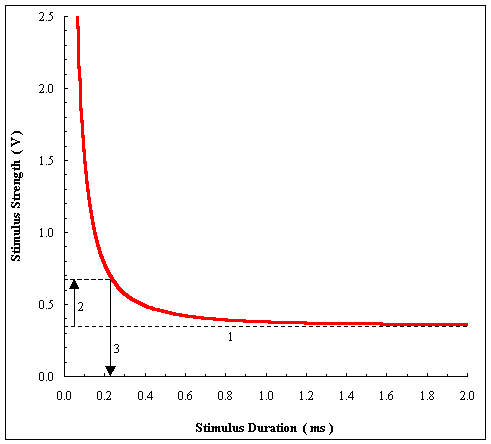
The following steps are followed in order to determine rheobase and chronaxie
Step 1 – determine the rheobase, which is the minimum Stimulus Strength that will produce a response. This is the voltage to which the Strength-Duration curve asymptotes. In the example above, this value is 0.35 V.
Step 2 – calculate 2´rheobase ( = 0.7 V in the above example).
Step 3 – determine chronaxie, which is the Stimulus Duration that yields a response when the Stimulus Strength is set to exactly 2´rheobase. In the example above, the chronaxie is 0.22 ms.
Here are a couple mnemonic hints to help you remember which term is which:
1. The root word “rheo” means current and “base” means foundation: thus the rheobase is the foundation, or minimum, current (stimulus strength) that will produce a response.
2. The root word “chron” means time and “axie” means axis: chronaxie, then, is measured along the time axis and, thus, is a Duration that gives a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice the rheobase strength.