| EKG Criteria Brief Review |
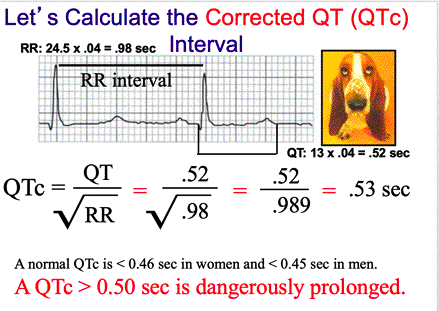
| Dear EKG Students, With this EKG Criteria Brief Review LINK I am attempting to help you Study/Learn/Know much of the essential 'key criteria' of EKG. Basic Criteria to Know: Always SHOW your UNITS One small box in seconds: .04 sec Normal PRI: .12 sec to .20 sec Accelerated PRI: less then .12 sec; or written this way < .12 sec Prolonged PRI: greater than .20 sec; or written this way > .20 sec Normal QRS: less than or equal to .12 sec; or written this way < .12 sec Abnormal QRS: greater than .12 sec; or written this way > .12 sec Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR): 60 to 100 bpm Sinus Arrhythmia: ~60 to ~100 bpm Sinus Tachycardia: >100 to ~150 bpm Sinus Bradycardia: less than 60 bpm; or written this way < 60 bpm Wandering Atrial Pacemaker: ~60 to 100 bpm Atrial Tachycardia (hidden P waves): 140 to 250 bpm Atrial Fibrillation (Afib) controlled: less than or equal to 100 bpm, or written this way < 100 bpm Atrial Fibrillation (Afib) uncontrolled: greater than 100 bpm, Also referred to as Afib RVR (rapid ventricular response); or written this way > 100 bpm Normal 'R' Wave transition: V3, V4 Early 'R' Wave transition: V1, V2 Late 'R' Wave transition: V5, V6 Junctional rhythm rate: 40 to 60 bpm Accelerated junctional rhythm rate: > 60 bpm to 100 bpm Junctional tachycardia: > 100 bpm Atrial Flutter Note: When writing Atrial Flutter interpretations, completely write them out. For example, Atrial Flutter with 3:1 AV Conduction, or, Atrial Flutter with Variable AV Conduction A Sinus Block (i.e., SA Block) is a multiple of R to R interval length (within plus or minus two small boxes) A Sinus Arrest (i.e., SA Arrest) is NOT a multiple of R to R interval length (it is GREATER THAN plus or minus two small boxes) Mean QRS Measurements to know. Write these out in full with correct charges Normal axis: -30 degrees to +100 degrees Right axis deviation: +100 degrees to ± 180 degrees Extreme right axis deviation: ± 180 degrees to -90 degrees Left Axis deviation: -90 degrees to -30 degrees Basic Terms to Know and Unique Morphology Characteristics to Remember Self-generating phenomenon of heart: pacemaker, automaticity, intrinsic, autorhythmic Foci: origin of pacemaker Overdrive suppression: one dominant pacemaker in the heart Only rhythm that sometimes has PARTIALLY hidden 'P' waves: Sinus Tachycardia Rhythm with Hidden 'P' waves is Atrial Tachycardia at 140 to 250 bpm Paroxysmal mean SUDDEN ONSE. Eample...NSR into Paroxysmal Atraila Tachycardia AV Blocks 1st Degree AV Block: Consistently prolonged PRI (PR interval > .20 sec). Example interpretation: NSR with a 1st Degree AV Block 2nd Degree AV Block Mobitz I: Progressively increasing PRIs until one QRS fails to depolarize after a P wave: Example interpretation: 2nd Degree AV Block Mobitz 1 2nd Degree AV Block Mobitz 2: PRIs are consistent (normal or prolonged) and do NOT lengthen: Conduction regularly converts to a 2:1 or 3:1 (look for EXTRA 'P waves' in 2:1 or 3:1 conduction). Example interpretation: 2nd Degree AV Block Mobitz II: 2:1 Conduction or 2nd Degree AV Block Mobitz II: 3:1 Conduction 3rd Degree AV Block: Complete heart block. PRIs are inconsistent length Ventricular Rhythms Heart Rate for IVR: 20 to 40 bpm Heart Rate for AIVR: >40 to 60 bpm Heart Rate for Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): >100 bpm There is no Heart Rate range for our class with Ventricular fibrillation (Vfib) There is no Heart Rate range for our class with Torsades de Pointes EKG Pioneers Augustus Waller: 1st electrical recording of heart; had pet Jimmy with him in lab Frank Wilson: Introduced the precordial leads Willem Einthoven: Introduced the first EKG (awarded Nobel Prize) Whilhelm His Jr: Discovered the Bundle of His William Harvey: Discovered blood flow in the human body Johannes Purkinje: Discoverd the purkinje fibers Jean Bachmann: Discoverd Bachmann's bundle Please make sure you can do a QTc calculation and Classify |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
|