| October 10 - October 14: EKG Primary Review, Introducing the PAC OBJECTIVES: Be able to correctly interpret the normal sinus rhythm, sinus tachycadia, sinus bradycardia, sinus arrhythmia, atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation Be able to correct identify and interpret the PAC Class, Please download the QUIZ First. We are working through MOST QUIZ questions in the YOUTUBE video lectures. Click Here to Download Quiz due Friday Oct. 14 by 12 Midnight (or sooner!) CLICK the links below and PRINT Worksheets #1, #2, #3, #4 Please CLICK this link and PRINT Worksheet #1 Please CLICK this link and PRINT Worksheet #2 Please CLICK this link and PRINT Worksheet #3 Class, after you complete Worksheet #3 please proceed to complete the interpretations on Worksheet #4 Please CLICK this link and PRINT Worksheet #4 Note to Class: There are 2 Youtube Videos with this Week (see below): Click here for the EKG Primary Review YOUTUBE lecture video Please DOWNLOAD Worksheet #1 (see above) and interpret rhythms 1-5 AFTER your watch the EKG Primary Review YOUTUBE video. Please DOWNLOAD Worksheet #2 (see above) and interpret the 12 lead EKG (Exam question #17). Then, watch the Introducing the PAC YOUTUBE video to check your work (below). |
||||||||
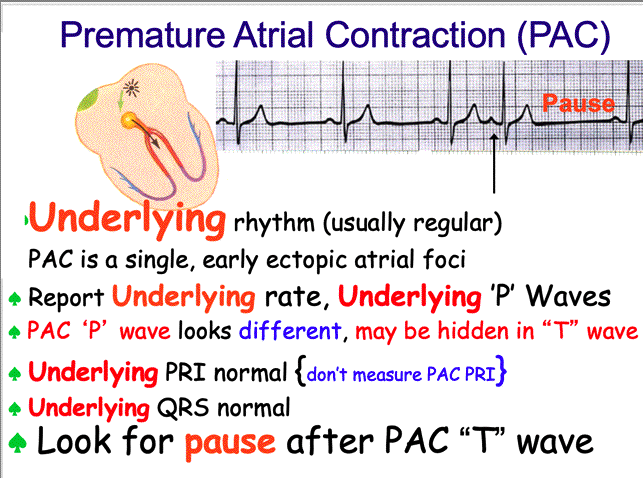
| Introducing the Premature Atrial Contaction (PAC) | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
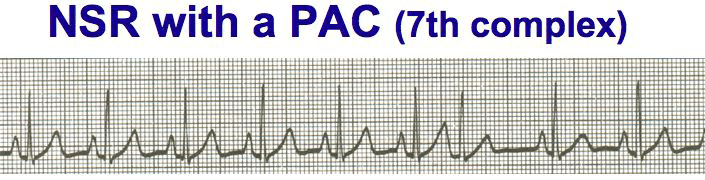
| CLASS, REMENDER YOU REPORT THE UNDERLYING RHYTHM, RATE, P WAVES, PRI AND QRS TO THE LEFT (i.e., BEFORE) OF THE PAC! THEN STATE WHERE THE PAC IS; IN THIS CASE IT IS THE 7th COMPLEX. | ||||||||
| Paroxysmal Rhythms | ||||||||
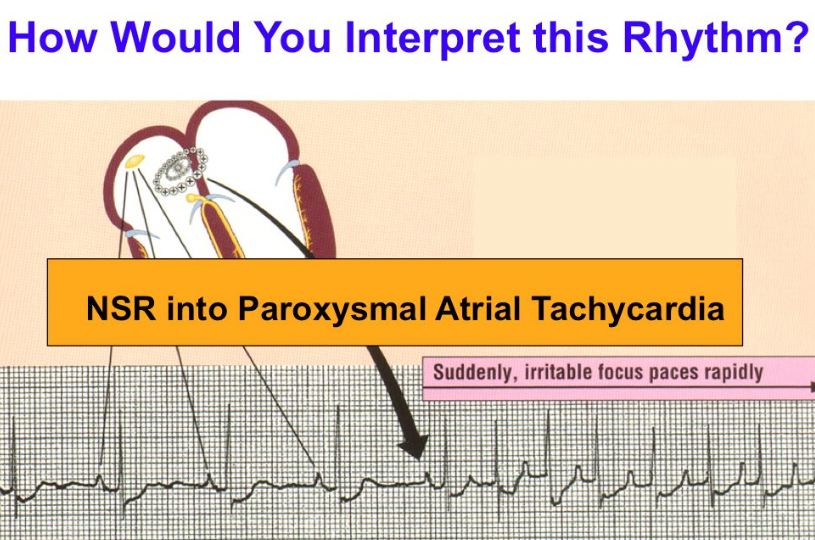
| Paroxysmal means sudden onset. In class, whenever you see a rhythm 'suddenly' get significantly faster (100 b/min or faster) this is a paroxysmal rhythm. For class, we will ONLY identify a paroxysmal rhythm when we see it (like below). Often times our textbook author will say this is a 'paroxysmal rhythm', meaning the author wanted you to know it suddenly happened. | ||||||||
| For the interpretation. Interpret a paroxysmal rhythm like TWO rhythms. Interpret the FIRST rhythm and then the Paroxysmal rhythm. Interpet like below: NSR into paroxysmal atrial tachycardia. | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
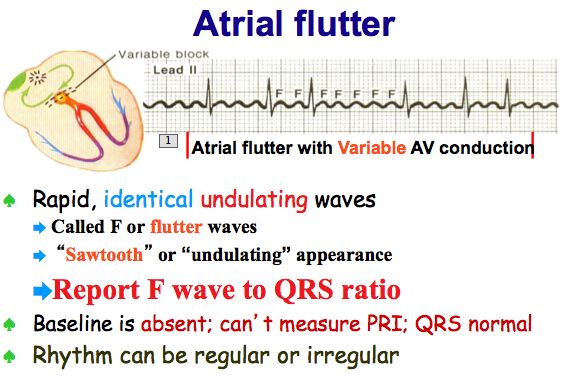
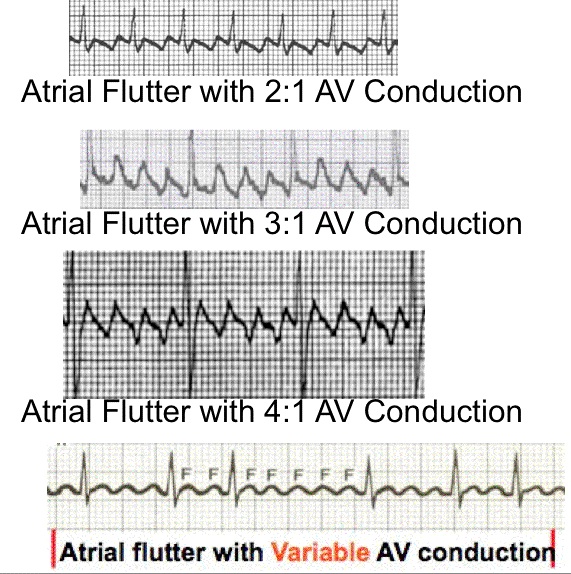
| With atrial flutter the 'P' waves are 'flutter' waves. The PRI is indeterminate. Note the 'Flutter' or 'F' waves. They often look like a 'saw tooth' as well. Baseline is absent. Report the F wave to QRS ratio. If not a consistent ratio it is called Atrial Flutter with Variable AV conduction (as seen above). | ||||||||
| Examples of Atrial Flutter | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
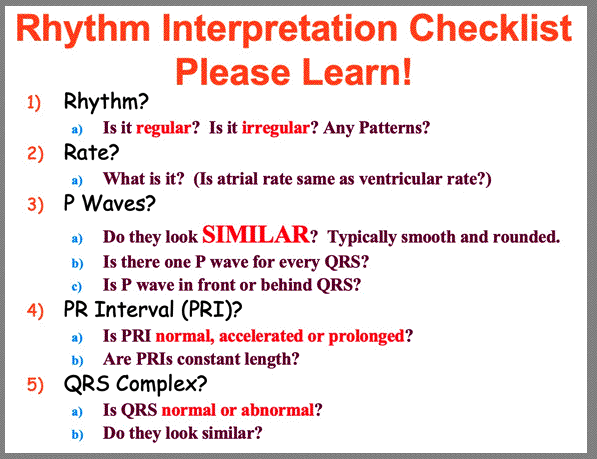
| Remember, After you go through the 5 steps of the Checklist you do your interpretation of the rhythm. | ||||||||
|