| January 19-22: Intro to PEP326L, Historical Roots of Exercise Physiology, Fitness Components, Homeostasis, Risk Factors & Negative Feedback OBJECTIVES: Be able to name several early pioneers of Exercise Physiology and discuss their contributions, including the following: Herodicus, Hippocrates, Glaude Galen, Archibald Hill, Lawrence Henderson, David B. Dill, Per-Olof Astrand, Bengt Saltin, Jonas Bergstrom, Albert Behnke, Thomas K. Cureton, J.C. Dalton, and Milo Be able to identify the first scientific conference in Sports Medicine and the year Be able to describe an acute response and a chronic adaptation Be able to name and define the 5 Components of Fitness Be able to explain what longitudinal research is and give an example Be able to describe homeostasis, steady state and negative feedback Be able to define 'risk factor' and give several examples Click Here to Download Exam 1 Part A due Friday January 22 by 12 Midnight SPECIAL NOTE: There are THREE YOUTUBE videos to watch on this page. Work yourself through the material. Let's start PEP326L off by watching this Introduction to PEP326L Fundamentals of Exercise Physiology YOUTUBE video. Dr. Kravitz discusses how the class will be taught this semester. He introduces the PEP326L Home WEB page that students will use this semester. You will be studying muscle physiology, nervous system physiology, respiration, cardiovascular physiology, metabolism and exercise endocrinology in Fundamentals of Exercise Physiology. Instructional strategies are discussed as well as the procedures for submitting weekly exams. Dr. Kravitz also describes his academic goals and academic integrity expectations for all students in PEP326L. Have a great semester. Click here for the Introduction To PEP326L YOUTUBE video We are ready for our first lecture on the Pioneers of Exercise Physiology and some foundational concepts. Click here to get started on our First YOUTUBE Lecture Below is a practice quiz of many of the pioneers in Exercise Physiology. See if you can match the name with the contribution of the pioneer: |
||||||||||||||
| Pioneer Matching Practice Quiz | ||||||||||||||
| Pioneers: Per-Olof Astrand, Milo, J.C. Dalton, Albert Behnke, Archibald Hill, Galen, David B.Dill, Lawrence Henderson, Hippocrates, Thomas K. Cureton, Jonas Bergstrom, Herodicus, Bengt Saltin | ||||||||||||||
| 1. Which pioneer excelled in Sports Medicine and even treated some of the Gladiators? 2. What scientist founded the Harvard Fatigue Laboratory? 3. Who is recognized as the 'father of preventive medicine'? 4. This pioneer had great impact on the physical fitness movement in the U.S. 5. What scientist developed the biopsy needle? 6. This scientist was known for his work in energy metabolism and was a Nobel prize winner. 7. This medical doctor was truly a visionary of health and fitness understandings accepted today. 8. This doctor was the mentor to Hippocrates. 9. The first and only director of the Harvard Fatigue Laboratory. 10. Researcher most associated with body composition investigations. 11. Scandinavian researcher who is recognized for work in muscle metabolism. 12. Which researcher who did much work on endurance capacity of runners? 13. Famous Greek Athlete credited with introducing 'Progressive Overload'? |
||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Check your answers below: | ||||||||||||||
| 1=Galen, 2=Lawrence Henderson, 3=Hippocrates, 4=Thomas K. Cureton, 5=Jonas Bergstrom, 6=Archibald Hill, 7=J.C. Dalton, 8=Herodicus, 9=David B.Dill, 10=Albert Behnke, 11=Bengt Saltin, 12=Per-Olof Astrand, 13=Milo | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Five Components of Fitness: Please be able to Name and Explain. Please learn on your own: WEB based learning experience. | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
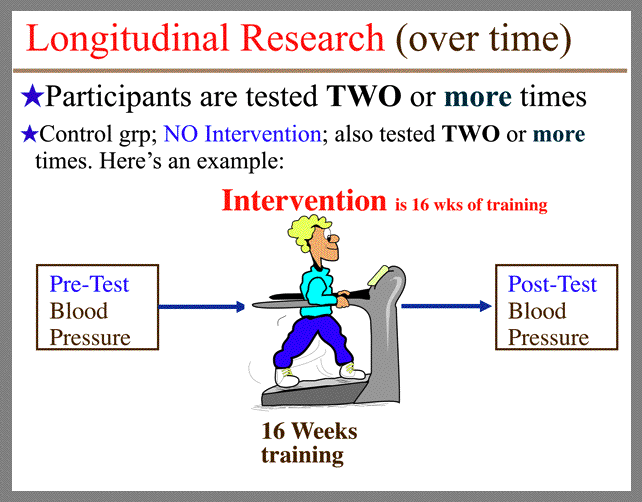
| Longitudinal Research, Homeostasis, Steady State and Negative Feedback | ||||||||||||||
| Class, here is what I call my Educational Buidling Blocks Youtube video which explains longitudinal research, risk factors, steady state and negative feedback. These are terms that will come up throughout the semester. Click here to watch the Educational Building Blocks YOUTUBE lecture |
||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||
| With Steady State and Homeostasis, some physiological variables of interest to measure include: heart rate, blood pressure, core body temperature, glucose metabolism and respiration rate. | ||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||
|