| March 22 to March 26: VO2 Max, Metabolic Adaptations to Aerobic and Anaerobic Exercise, and Neuromuscular Fatigue OBJECTIVES: Be able to define VO2 max and why is it important Be able to explain the criteria for VO2 max Be able to discuss the metabolic adaptations to aerobic exercise Be able to discuss the metabolic adaptations to anaerobic exercise Be able to define neuromuscular fatigue and describe mechanisms contributing to it at the neuromuscular junction and within skeletal muscle Please note there are FOUR YOUTUBE videos with this week's lessons. For Exam 3 Part A Click Here: Please download in advance to answer questions. Let's start by watching this short Youtube video the explains VO2max and respiratory exchange ratio or RER. VO2Max and Respiratory Exchange Ratio YOUTUBE video Please now watch this short Youtube video that discusses maximal heart rate, ratings of perceived exertion (RPE), and plateau of less than or equal to 150 ml oxygen/min Maximal Heart Rate, RPE and VO2Plateau YOUTTUBE video What is VO2 max (sometimes written VO2max) and why is it important? VO2 max, also called maximal aerobic capacity, is the maximal consumption, distribution and utilization of oxygen by the body. Understanding VO2 max tests a little deeper. Maximal aerobic capacity tests are often used in fitness setting to monitor change over time of the cardiorespiratory system. Certain exercise programs, such as high intensity interval training (HIIT) have been show to be most effective in improving VO2 max. Typically, in a laboratory setting the exercise physiologist will design a workload for the VO2max so the person attains it in 8-12 minutes. If the test goes longer than 12 minutes, the client may tire of exhaustion prior to attaining her/his actual VO2max. As well, there is a quite a bit of recent research that shows the higher your VO2 max, the lower your risk to cardiovascular disease. Therefore, the big takehome message for all people is regardless of your fitness level, try to keep improving your aerobic capacity for a healthier quality of life. Please learn the criteria for attaining VO2 max. In a laboratory testing situation there are some standardized criteria to verify whether a person has attained VO2max. These criteria include RER> 1.15, ±10 beats/min of predicted maximal heart rate (MHR), plateau of &Mac178; 150 ml oygen/minute and an RPE > 17. The theoretical limits of RER are from .7 to 1.0. What would be the estimated maximal heart rate (estimated MHR) for a 20 year-old male or female? Although there are several equations to predict maximal heart rate, we will use the equation of 220-AGE = Estimated maximal heart rate.Therefore, the estimated MHR for a 20 year-old male or female is 220-20 = 200 (Estimated MHR) With a VO2 peak, a person gives an 'all-out' effort during a maxial aerobic test, but doesn't attain any of the criteria. This is called a VO2 peak. Please examine and review the slide below defining VO2 max and the four established criteria to know if it has been attained. |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
| RER represents respiratory exchange ratio. This is the ratio of CO2 expired to O2 consumed Predicted (or estimated) maximum heart rate is 220-Age. So, a predicted maximum heart rate for a 20-year-old student is 220-20=200 beats per minute. Remeber, we look at heart rate in beats per minute. Plateau of VO2 means the following: A maximal aerobic test progressively gets harder for the sujbect. When the oxygen consumption (VO2) plateaus < 150 ml oxygen/min as the test continues to get harder it is a very good indicator that the subject is at or near their actual VO2max capacity (i.e, ceiling). Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE). RPE is a person's subjective assessment of how hard they are working during an exercise bout.. We used a technique called 'anchoring,' which is explaind in one of your Youtube videos to each participants how to effective use the RPE chart (from 6 to 20). This RPE chart was developed by Dr. Gunnar Borg (some people to this day call it the Borg scale) Although VO2 peak (also written VO2peak) varies from textbook to textbook, for PEP326L a VO2 peak test is when a subject gives a maximal effort in an aerobic capacity test but does NOT attain any of the criteria. It means the subject worked as hard as she/he could, but did not attain any of the VO2max criteria. |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| What are the Metabolic Adaptations to Aerobic Exercise? | ||||||||
| Class, please watch this Youtube video which explains the metabolic adaptations to aerobic exercise. | ||||||||
| Metabolic Adaptations to Aerobic Exercise YOUTUBE Video Class, below is a summary slide of metabolic adapations from aerobic exercise. |
||||||||
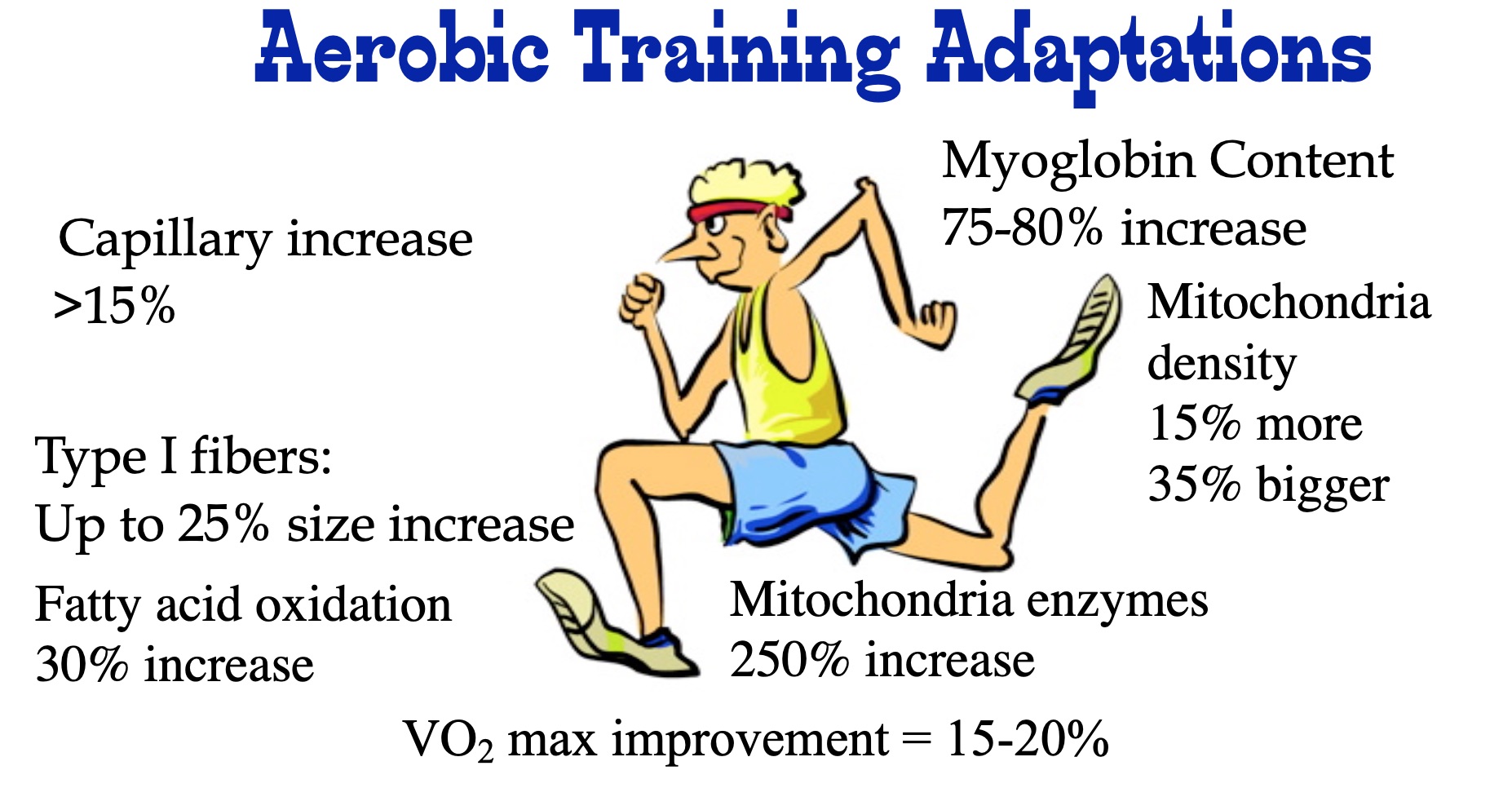 |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| What are the Metabolic Adaptations to Anaerobic Exercise? |
||||||||
| Class, please watch this Youtube video which explains the metabolic adaptations to anaerobic exercise. |
||||||||
| Metabolic Adaptations to Anaerobic Exercise YOUTUBE video Class, below is a summary slide of metabolic adapations from aerobic exercise. |
||||||||
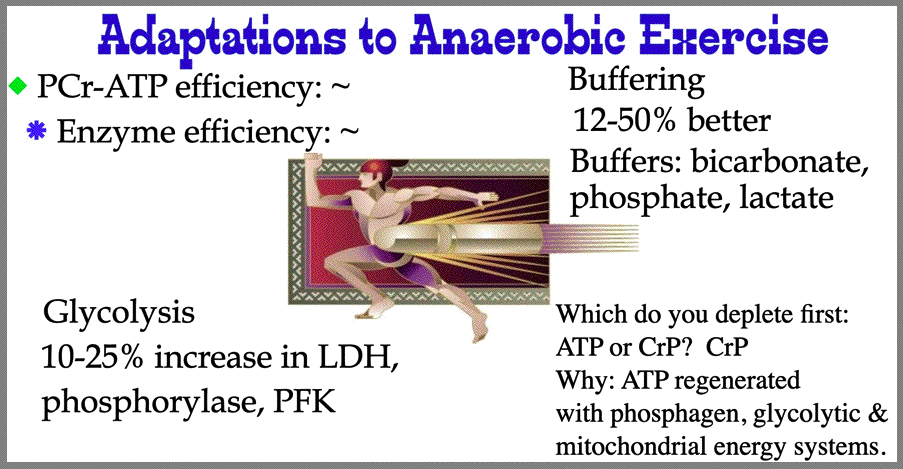 |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Special Topic: Skeltal Muscle Fatigue | ||||||||
| The physiological contributions to fatigue are multifactorial. With this WEB based learning experience we are laser focusing on Peripheral Fatigue mechanisms. Let this section guide your answers to exam questions on fatigue. | ||||||||
| What is Neuromuscular fatigue? Neuromuscular fatigue can be defined as any exercise-induced decrease in a muscle's ability to develop force or power? Explain the TWO TYPES of neuromuscular fatigue? CENTRAL fatigue is the signal message from the brain to the neuromuscular junction. PERIPHERAL FATIGUE is the signal messages from the neuromuscuscular junction to muscle and within the muscle. Explain the mechanism of neuromuscular fatigue at the neuromuscular junction? At the neuromuscular junction there is a breakdown of ACh in getting to the motor end plate, thus the action potential does not reach the motor end plate. Therefore, the muscle contraction will not be able to continue. |
||||||||
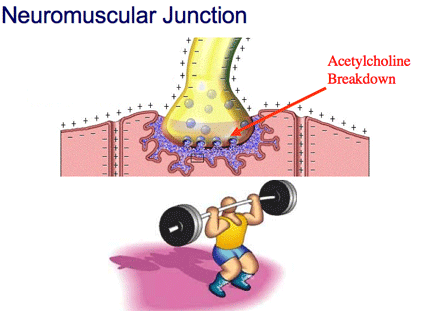 |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Within Muscle there are Two Sites that Contribute to Fatigue. Within muscle, explain how H+ (hydrogen ions) interfere with calcium ions, and thus contibute to fatigue? The H+ ions (from the hydrolysis of ATP) interfere with calcium ions from binding to troponin. The interference PREVENTS the configuration shift of tropomyosin to reveal the active bindings sites. Therefore the myosin S1 units will not bind to the actin molecule and muscle force production will decrease. Within muscle, explain how acidosis contributes to fatigue? The increase in acidosis (from the H+ ion accumulation) will denature (i.e., breakdown or unfold) the enzyme ATPase. This inhibits the splitting of ATP to ADP and Pi and energy and thus muscle force production decrases. Importantly, the H+ accumulation is coming from the hydrolysis of ATP during the exercise bout. The H+ comes from the water molecule (H2O). |
||||||||
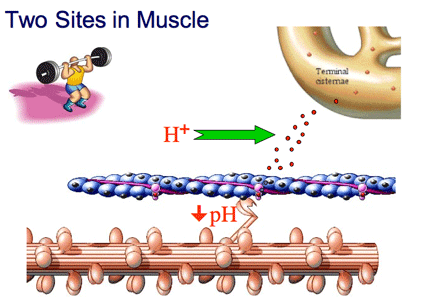 |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
|